Samurai Sword Tsuba

Japanese Sword mountings include saya, kashira, seppa, fuchi, habaki, menuki, tsuba etc. The tsuba (鍔, or 鐔) is a guard at the end of the grip of bladed Japanese weapons, which is mostly meant to be used to prevent the hand from sliding onto the blade of a Japanese sword. The tsuba is the main mounting which has a leading position in terms of value, circulation, and artistry, especially in the United States, European countries, Japan. Although it belongs to the accessories of Japanese swords, it is an independent single item in the collection field. In other words, sword and tsuba are two independent art.
The key of producting a good tsuba is the choice of materials, ingenious and creative design style, appropriate composition and space allocation, concise construction technology, a good state of preservation etc. The tsuba usually can be made of alloy, iron, brass.
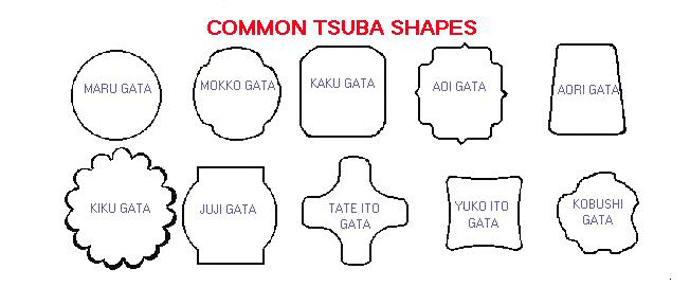
The tsuba shape is usually round (maru gata), rounded-square (kaku gata) and four lobed (mokko) with many variations within each basic design. The patina (surface coloration) gives the tsuba its beauty. Clean tsuba will remove the patina and destroy the beauty and value of the item.



Leave a Comment